Battery Reset Impact Simulator
Simulation Results
Quick Summary / Key Takeaways
- Removing or resetting the battery battery reset erases stored data in the vehicle’s control modules.
- The fuel pump itself does not get reset, but the Engine Control Module (ECM) may relearn fuel delivery settings.
- Most modern cars need a specific reset sequence or a diagnostic tool to clear error codes after a battery disconnect.
- If you’re facing a no‑start condition, try the full reset steps before swapping parts.
- Always consult the vehicle’s service manual - a wrong move can leave you stranded.
Ever wondered if pulling the battery cables will magically fix a stubborn fuel pump? You’re not alone. Many DIYers assume that a simple battery reset is a quick way to clear glitches in the car’s electronics will also clear any issues with the fuel pump. The short answer: the pump itself isn’t “reset” by the battery, but the electronic brains that control it-primarily the Engine Control Module (ECM) and, in some models, the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)-do get a fresh start. Let’s break down what really happens, when a battery disconnect matters, and the safest way to reset everything without guessing.
How a Battery Reset Works
The moment you disconnect the negative terminal, you cut power to every electronic component that relies on the 12‑volt system. That includes the ECM the computer that manages fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions controls and the PCM a broader controller that oversees both engine and transmission functions in many newer cars.When power returns, these modules reboot. They lose any stored trouble codes, learned idle parameters, and fuel trim values. In other words, the car forgets the “lessons” it gathered while you were driving. That’s why you often notice a brief period of rough idle or a “check engine” light that flips off after a few drive cycles.
Why the Fuel Pump Isn’t Directly Reset
The fuel pump is a mechanical device-usually an electric motor that pushes gasoline from the tank to the injectors. It has no memory or software to clear. Its operation is governed by voltage from the fuel pump relay an electromagnetic switch that tells the pump when to run and the commands it receives from the ECM.
When you pull the battery, the relay loses power and the pump stops, but the pump’s performance characteristics (flow rate, pressure) stay the same. The only thing that can change is how the ECM tells the pump to behave once power returns.
Does Resetting the Battery Reset the Fuel Pump?
In practical terms, no-resetting the battery does not reset the fuel pump hardware. However, the ECM does lose its “fuel map” memory, which means the next time you start the engine it will use default fuel delivery settings. For most healthy pumps, this has no negative effect; the ECM quickly re‑learns the correct fuel trim during the first few minutes of driving.
What can happen is that a stored fault code related to the pump-like a low‑pressure warning-gets cleared. If the underlying issue still exists (blocked filter, weak pump, or wiring fault), the code will pop right back on the next drive cycle, often accompanied by a limp‑mode response.
When a Battery Reset Can Influence Fuel Pump Behavior
Here are the most common scenarios where a battery disconnect will impact the fuel pump indirectly:
- After replacing a fuel pump relay. The ECM may need to re‑learn the relay’s timing, so a full battery reset helps the system accept the new part.
- When troubleshooting a no‑start condition. A dead or weak battery can cause low voltage to the pump, preventing it from building pressure. Resetting the battery and recharging it often restores proper voltage.
- Following a major ECM/PCM flash. Flashing new software wipes the learned fuel maps, and a battery reset ensures the module starts from a clean slate.
- During seasonal storage. Long‑term storage can cause battery drainage; disconnecting it prevents parasitic draw, and the ECM will re‑learn idle and fuel trim when you’re ready to drive again.
Step‑by‑Step Battery Reset Procedure (Safe & Effective)
- Park the car on a flat surface, engage the parking brake, and turn off all accessories.
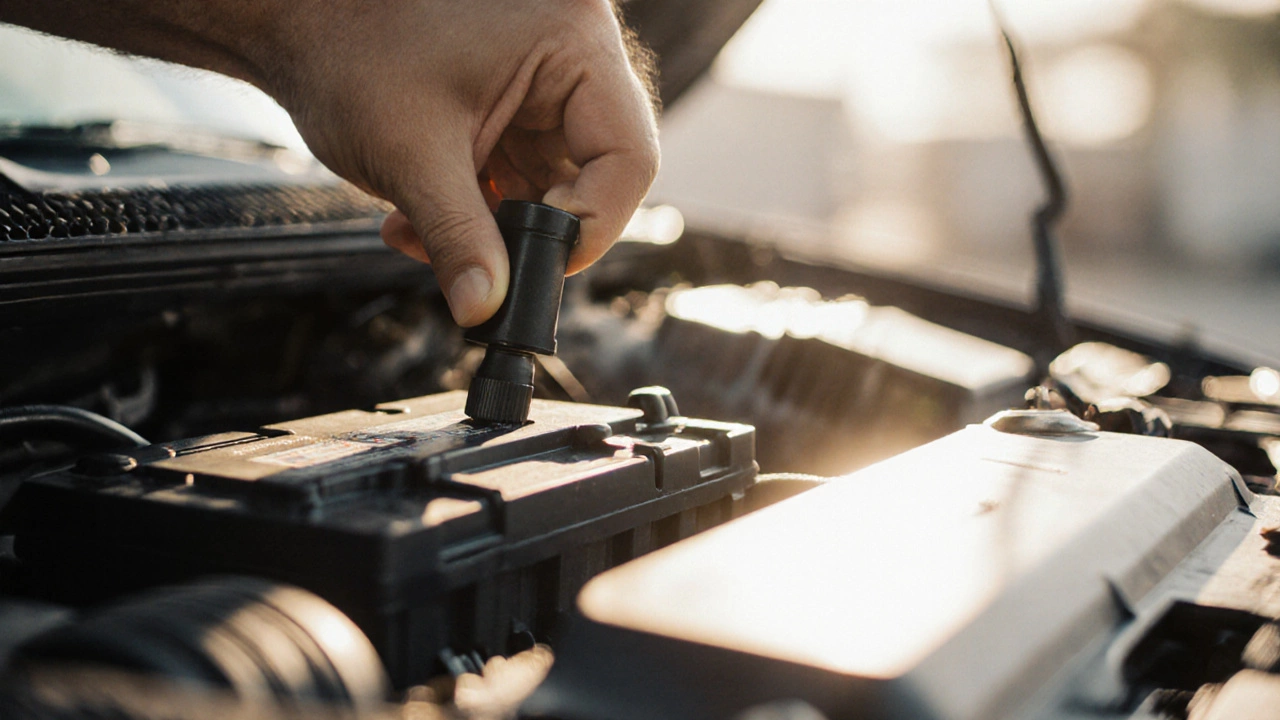
- Open the hood and locate the negative (‑) battery terminal. It’s usually marked with a black cable.
- Using a 10mm wrench, loosen the terminal bolt and remove the cable. Push it aside to avoid accidental contact.
- Leave the battery disconnected for at least 10minutes. This window lets all capacitors within the ECM and PCM bleed off residual charge.
- While you wait, press the brake pedal a few times. This helps discharge any remaining voltage stored in the vehicle’s CAN bus.
- Reconnect the negative cable, tighten the bolt snugly, and close the hood.
- Turn the ignition to the ON position (do NOT start the engine). Watch for any warning lights; if a “check engine” remains lit, note the code with an OBD‑II scanner a diagnostic tool that reads trouble codes from the ECM.
- Start the engine. Expect a slightly rough idle for the first 30‑60seconds as the ECM re‑learns idle speed and fuel trim.
That’s it-no fancy tools required. If the engine still won’t start or the fuel pump seems unresponsive, the problem likely lies elsewhere (fuel filter, pump itself, or wiring).

Alternative Ways to Reset the Fuel Pump Circuit
Sometimes you need to target the fuel pump without disconnecting the whole battery. Here are three proven methods:
| Method | Tools Needed | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Pump Relay Pull | Fuse/relay box diagram, pliers | After relay replacement or to clear a temporary fault |
| ECM Reset via OBD‑II | OBD‑II scanner with reset function | When you have stored codes you want to clear without a full battery disconnect |
| Manual Pump Priming | Key ignition, screwdriver (to access pump relay) | When the pump isn’t receiving voltage after a recent battery change |
Using the relay method, you simply remove the fuel pump relay for 5seconds, then replace it. The ECM treats this as a power‑cycle for the pump circuit, which can clear minor glitches. An OBD‑II reset, on the other hand, erases trouble codes and forces a re‑initialization of fuel parameters without losing other learned data like transmission shift points.
Common Pitfalls & Pro Tips
- Pitfall: Forgetting to wait 10minutes. Some modern modules hold charge for up to several minutes; cutting the time short can leave residual data lingering.
- Pro tip: Use a memory saver (a small 12V battery pack) if you need to keep radio presets, clock, or ECU data intact while performing a battery swap.
- Pitfall: Re‑connecting the positive terminal first. This can cause a short if the negative clamp is still loose.
- Pro tip: After a reset, drive the car for at least 5minutes at steady highway speeds. That gives the ECM enough data to fine‑tune fuel trims.
- Pitfall: Assuming a cleared code means the problem is solved. Always verify fuel pressure with a gauge if the original symptom was low‑pump pressure.
Checklist: Is a Battery Reset Enough?
- Did the issue appear after a battery change or electrical work? - Yes → Try a full reset.
- Is the check engine light flashing with a P0087 (fuel rail pressure) code? - Yes → Inspect pump and fuel rail before resetting.
- Do you hear the pump whirring when turning the key to ON? - No → Check fuse, relay, and pump wiring.
- Is the battery voltage above 12.6V after charging? - No → Recharge or replace the battery first.
- After reset, does the idle smooth out within a minute? - No → There may be a deeper ECU learning issue.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will a dead battery always cause the fuel pump to stop?
Yes. The pump needs at least 9-10V to build pressure. If the battery voltage drops below that, the pump can’t spin fast enough and you’ll get a no‑start or stalling condition.
Do I need to reset the ECM after replacing a fuel pump?
Not always. Most modern ECUs will adapt on their own. However, clearing the codes with an OBD‑II scanner or doing a full battery disconnect can speed up the learning process and erase any lingering pump‑related trouble codes.
Can a faulty fuel pump relay mimic a bad battery?
Absolutely. If the relay sticks open, the pump never receives power, and the engine behaves as if the battery is dead. Swapping the relay or tapping it to test can quickly diagnose the issue.
Is it safe to use a memory saver while doing a battery reset?
Yes. A memory saver keeps the ECU powered, preserving learned adaptations like transmission shift points and radio presets. Just connect it to the positive terminal after you unplug the negative cable.
How long does it take for the ECM to relearn fuel trim after a reset?
Typically 5‑10 minutes of varied driving (city, highway, idle). The ECU gathers data from the oxygen sensors and adjusts the trim until it stabilizes.




